- Anatomy
- Conditions
- Procedures
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery
Minimally invasive spine surgery (MISS) is the latest technology available to perform spinal surgeries through small, less than one-inch-long incisions. It involves the use of special surgical instruments, devices and advanced imaging techniques to visualize and perform the surgery through such small incisions.
Robotic Spine Surgery
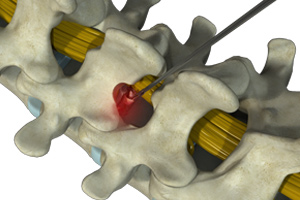
Robotic spine surgery is a procedure where your surgeon is assisted by a robotic system to perform surgery to the spine. Precision is very important when performing spine surgery. Robotic systems are becoming increasingly popular in the medical fraternity as it offers better precision and reduces the risk of complications associated with conventional surgery. Your doctor can use robotic assistance while performing an open or minimally invasive procedure.
Lumbar Discectomy
A lumbar discectomy is a surgical procedure performed to treat a herniated or ruptured disc and relieve pressure on the spinal nerves.
Microdiscectomy
Microdiscectomy, also called microdecompression, is a minimally invasive spinal surgery where your surgeon removes a part of the herniated disc to relieve pressure on the spinal nerves.
Cervical Disc Replacement
The cervical spine is located in the neck region and consists of seven bones arranged one on top of the other. Cushioning tissue called vertebral discs located between the vertebrae act as shock absorbers, allowing easy movement of the neck. Wear and tear and advancing age can damage these discs, leading to pain and disability. Artificial cervical disc replacement surgery is a procedure where the damaged intervertebral disc is removed and replaced with an artificial implant. The surgery relieves neck pain as well as restores the normal range of motion of the neck.
Spinal Fusion
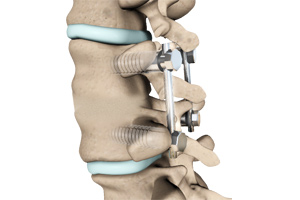
Spinal fusion is the surgical technique of combining two or more vertebrae. A fusion of the vertebrae involves the insertion of secondary bone tissue obtained either from an autograft (tissues from your own body) or allograft (tissues from another person) to enhance the bone healing process.
Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion (OLIF)
Lumbar interbody fusion can be performed through different approaches. Oblique lumbar interbody fusion (OLIF) is a minimally invasive approach to LIF, where an incision is made on your side to avoid damaging important muscles and ligaments in your back.
Image-Guided Spine Surgery
Imaging techniques such as computed tomography and fluoroscopy may be integrated into the system to facilitate pre-operative planning of the surgery, where a series of images taken before the surgery are displayed on a screen, with which your surgeon matches his/her moves intraoperatively. They can also serve as real-time guidance, where your surgeon can view, and navigate instruments and implants as they are placed during the surgery.
Scoliosis Surgery
Surgery for scoliosis is recommended when the spinal curvature is severe and is either worsening or is a cause of severe pain or difficulty in breathing. The surgery is aimed at rectifying the spinal curvature, stabilizing the spine and preventing it from worsening. The rectification of the curved spine involves the removal of one or more intervertebral discs (disectomy), vertebrae, or spinous processes from the curved segment of the spine. The gaps in the bones are then filled with a bone graft. Ribs can be a source of the bone graft. Rods and screws are used to permanently fix the spine in the rectified position.
Posterior Scoliosis Surgery
The goal of scoliosis surgery is to both reduce the abnormal curve in the spine and to prevent it from progressing further and getting worse. To achieve this, a spinal fusion is performed to fuse the vertebrae within the curve to be corrected. This involves placing bone graft or bone graft substitute in the intervertebral space between the two vertebrae. Instrumentation such as rods and screws are also used to realign and stabilize the vertebrae until the graft heals and fuses the two vertebrae together.
Adult Scoliosis Correction
Adult scoliosis is the abnormal curvature of the spine giving the spine an “S” or “C” shape in a skeletally mature person. Larger curves cause discomfort while smaller curves usually do not cause any problems. In most cases, the exact cause remains unknown. However, adult scoliosis can develop as a result of:
Spinal Decompression
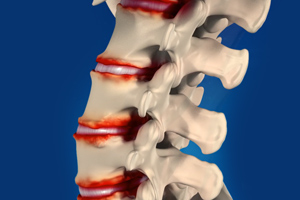
Spinal decompression is a treatment to relieve pressure on one or many “pinched nerves” in the spinal column. It can be achieved either surgically or by non-surgical methods. Spinal decompression is used to treat conditions that cause chronic backaches such as herniated disc, disc bulge, sciatica, and spinal stenosis.
Spine Deformity Surgery
Spine deformity can be defined as abnormality in the shape, curvature, and flexibility of the spine. When the curves are exaggerated, pronounced problems can occur such as back pain, breathing difficulties and fatigue.
Degenerative Spine Surgery
Degenerative spine surgery includes surgical procedures to treat degenerative spine conditions such as disc disease and spinal stenosis that can result in the gradual deterioration of the spine with pain and loss of function. Degenerative spine surgery may involve removal or replacement of the spinal discs, surgery to relieve nerve compression, or fusion of the vertebrae to improve spine stability.
Spine Osteotomy
Spine osteotomy is a surgical procedure in which a section of the spinal bone is cut and removed to allow for correction of spinal malalignment.
Complex Spinal Surgery
Complex spine surgery is a type of back surgery involving a fusion of six or more vertebrae. The vertebrae are a series of small interlocking bones extending from the skull to the pelvis (hip) to form your spinal column or backbone. Spinal fusion helps in forming a solid bridge of bone that stabilizes your back. The surgery may involve the placement of screws and rods within the spine and may take six hours or longer to complete.
Computer-Assisted Spine Surgery
Computer-assisted spine surgery is an instrument tracking technology in which the surgical instruments are viewed with the help of three-dimensional images of the spine. This technology increases the accuracy and safety of the spinal procedures which cannot be achieved with traditional spinal surgical approaches.
Disc Decompression
Acute or chronic injury can cause a spinal disc to herniate or rupture. The damaged disc may compress against the spinal cord or the nerves that branch out through the vertebral bones, leading to pain, loss of sensation and/or motor function in the part of the body supplied by the nerve. Disc decompression is a surgical procedure to release pressure on the compressed nerve by removing a part of the damaged disc (discectomy).
Lumbar Fusion
Spinal fusion, also called arthrodesis, is a surgical technique used to join two or more vertebrae (bones) within the spine. Lumbar fusion is the procedure of fusing the vertebrae in the lumbar portion of the spine (lower back). A piece of bone, taken from other parts of the body or donated from a bone bank is transplanted between the adjacent vertebrae. Screws, plates, or cages may be used with the bone graft to help hold the spine.
Posterior Lumbar Fusion
The surgery can be performed as an open or laparoscopic (keyhole) surgery. Posterior spinal fusion is a procedure where your surgeon makes an incision on your back to expose the spine. The soft tissues and blood vessels are kept apart to avoid damage.
Lumbar Interbody Fusion
Lumbar interbody fusion (LIF) surgery is a surgical technique that involves the removal of a damaged intervertebral disc and the insertion of a bone graft into the disc space created between the two adjoining vertebrae. Bone grafts promote healing and facilitate fusion. Screws and rods are used to stabilize the spine during the healing process.
Lumbar Decompression
Lumbar decompression is a surgical procedure performed to relieve pressure over the compressed nerves in the lower spine (lumbar region).
Anterior and Posterior Scoliosis Surgery
The spine is the backbone of the body. It naturally curves a little. This allows us to walk, move and balance ourselves properly. But some people have a spine that curves too much to one side. This condition is called scoliosis. In most cases, especially in children and adolescents, the cause of scoliosis is unknown and scoliosis is referred to as idiopathic scoliosis.
Minimally Invasive Lumbar Discectomy
Lumbar discectomy is a spinal surgery that involves the removal of the damaged intervertebral disc(s) to relieve pressure on the spinal nerves (decompression) in the lumbar (lower back) region, which forms the lower portion of the spine and comprises of five vertebrae (L1-L5). A minimally invasive technique is implemented to perform the surgery.
Minimally Invasive Discectomy and Decompression
The spinal cord passes through the vertebral column, which forms a bony protective cover. However, many conditions can cause parts of the vertebrae to compress the spinal cord or the nerves that branch out through them, leading to pain, loss of sensation and/or motor function in the part of the body supplied by the compressed nerve. Minimally invasive discectomy and decompression is a surgical procedure to release pressure on the compressed nerve and restore function.
Minimally Invasive Lumbar Decompression
Minimally invasive lumbar decompression or mild® is a procedure developed by Vertos Medical to treat lumbar spinal stenosis by relieving pressure on the spinal nerves.
Minimally Invasive Lumbar Fusion
Spinal fusion is a surgical technique used to join together two or more vertebrae in the spine and to minimize the pain caused by the movement of these vertebrae. The fusion of vertebrae in the lumbar portion of the spine is called lumbar fusion and the surgery can be done as an open or minimally invasive procedure.
Lumbar Microdecompression
Lumbar microdecompression, also known as lumbar microdiscectomy, is a minimally invasive surgical procedure to relieve pressure from pinched nerves in the lower back or lumbar region using microsurgical techniques. The procedure involves the removal of a small section of the bone and/or disc material pressing on the spinal cord and/or nerve roots in the lumbar spine to relieve painful symptoms.
Cervical Spine Fusion
Cervical spine fusion is a surgery performed to fuse weak cervical vertebrae with adjacent vertebrae to provide stability and prevent injury to the spinal cord.
Posterior Cervical Fusion
Posterior cervical fusion (PCF), a surgical procedure performed through the back of the neck, involves joining or fusing two or more damaged cervical vertebrae. The fusion of vertebrae is also known as arthrodesis. Sometimes, metallic plates may be used for fixing the vertebrae, this is also known as instrumentation.
Cervical Laminectomy and Fusion
During the procedure, your surgeon makes an incision in the center, at the back of your neck. The muscles are moved aside, the arteries and nerves in the neck are secured. Once the access to the spine is gained, the lamina of the affected vertebra is removed along with the bone spurs if present. Sometimes, cervical fusion surgery is done along with cervical laminectomy procedure. This is to prevent the risk of developing spinal instability that may lead to pain.
Cervical Microdiscectomy
Your spine consists of 24 bones called vertebrae that are arranged one above the other and separated by intervertebral discs which act as shock absorbers during activity. Your neck or cervical area is made up of seven of these vertebrae. The intervertebral discs consist of 2 parts, namely annulus fibrosus (outer flexible ring) and nucleus pulposus (central soft jelly-like region). The discs can be damaged due to wear and tear or a sudden injury to the spine and is termed as a herniated disc. In this condition, the nucleus of the disc pushes against the outer annulus fibrosus and pinches the cervical nerves of the spinal cord that pass through these bones, causing pain in the arm. Cervical microdiscectomy is a surgical procedure performed to treat herniated discs in the cervical region.
Artificial Cervical Disc Replacement
Artificial cervical disc replacement is a spine surgery to replace a degenerated (deteriorated) disc in the neck with an artificial disc. The artificial disc, like the natural healthy disc, is used to replace the degenerated disc. It restores the height between the two cervical vertebrae, enlarging the neural foramen (nerve passageway in the spine) and relieving the pressure on the spinal nerves. This stabilizes the cervical spine and restores normal mobility of the neck.
Anterior Cervical Discectomy with Fusion
Anterior cervical discectomy with fusion is an operative procedure to relieve compression or pressure on nerve roots and/or the spinal cord due to a herniated disc or bone spur in the neck. The vertebra is approached from the from (anterior) of your neck.
Minimally Invasive Cervical Discectomy
A cervical discectomy or decompressive spinal procedure is an operative procedure that relieves pressure on the spinal nerves and/or spinal cord by partially or completely removing the intervertebral disc that is herniated and/or bony material (bone spur). Cervical discectomy can be performed using a minimally invasive approach if you are suitable.
Minimally Invasive Scoliosis Surgery
The goal of scoliosis surgery is to both reduce the abnormal curve in the spine and to prevent it from progressing further and getting worse. To achieve this, a spinal fusion is performed to fuse the vertebrae, in the curve to be corrected. This involves placing bone graft or bone graft substitute in the intervertebral space between the two vertebrae. Instrumentation such as rods and screws are also used to realign and stabilize the vertebrae until the graft heals and fuses the two vertebrae together.
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery for Spondylolisthesis
Spondylolisthesis is a condition of the spine characterized by the forward displacement of a vertebra over an underlying vertebra. A significant displacement can cause a compression of the spinal nerves resulting in pain. The two most common types of spondylolisthesis include dysplastic spondylolisthesis and isthmic spondylolisthesis.