- Anatomy
- Conditions
- Procedures
Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a condition characterized by the abnormal curvature of the spine that causes a deviation to one side. It causes a physical deformity, making the spine look like the letter “C” or “S” instead of the letter “I”. Scoliosis can affect either the mid or lower back. Scoliosis of the mid back is more common. Scoliosis can occur at any age.
Kyphosis
Kyphosis is a condition of abnormal curvature of the spine that causes rounding of the upper back or a hunchback. The thoracic portion of the spine normally has a C-shaped curve, but excessive forward curve in the spine leads to kyphosis. Kyphosis most commonly affects the thoracic spine, but can involve the cervical and lumbar portions too.
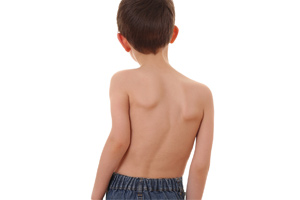
Scoliosis in Children
Scoliosis is an abnormal, sideways curvature of the spine. It is often diagnosed between infancy and early adolescence.
Cervical Stenosis
Cervical stenosis refers to the narrowing of the spinal canal that protects the spinal cord and its branching nerves.
Lumbar Stenosis
Lumbar stenosis is the compression of spinal nerves caused by the narrowing of the spinal canal. It is one of the common causes of lower back pain. Spinal stenosis can also affect the spine in the neck region.
Cervical Degenerative Disc Disease
Cervical degenerative disc disease (DDD) is a misnomer, as it is not a disease as such but a condition that affects the strength, resiliency and structural integrity of the intervertebral discs due to increasing age, trauma, injury, repetitive movement, improper posture, or poor body mechanics. Cervical DDD is commonly seen in adults after 50 years of age and most of them are usually not aware about their condition until they are examined for some other health condition.
Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease
Lumbar degenerative disc disease (DDD) is a common cause of lower back pain. Over time, these natural shock absorbers wear out and degenerate. Degenerative disc disease is not actually a disease but refers to the changes in the spine that occur as a part of the normal aging process.
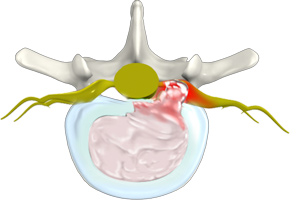
Disc Herniation
Disc herniation is a condition where the central nucleus pushes through the outer edge of the disc, causing a bulge that compresses the spinal nerves.
Spondylolisthesis
Spondylolisthesis is the displacement of the vertebral disc from the spinal column. Outward (forward) displacement is termed as anterolisthesis and inward (backward) displacement is termed as retrolisthesis. This condition is often preceded by spondylolysis, a degenerative condition of the vertebra.
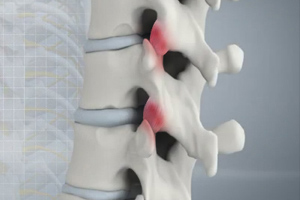
Degenerative Disc Disease
Degenerative disc disease (DDD) refers to the gradual deterioration of the intervertebral discs between the vertebrae. DDD is a misnomer as it is not actually a disease but a condition that affects the strength, resilience and structural integrity of the intervertebral discs due to advancing age, trauma, injury, repetitive movement, improper posture or poor body mechanics. DDD is commonly seen in individuals over 50 years of age. Most of them are usually not aware of their condition until they are examined for some other related health condition.
Flat Back Syndrome
The spine has three natural curves when viewed from the side, an inward curve in the neck and lower spine called lordosis and an outward curve in the mid-back called kyphosis. Normal spine curvature keeps your head in line with your pelvis so that the stresses on your spine are well balanced. Certain medical conditions, however, affect the curvature of the spine so that the curves become too flat or too pronounced. This changes the relationship of the head and the pelvis resulting in an imbalance of the spine called sagittal imbalance.
Cervical Radiculopathy/Myelopathy
Disc protrusions in the cervical or neck area place pressure on nerve roots (nerve root compression) or the spinal cord causing radiculopathy. Radiculopathy is a medical term used to describe the neurological deficits that can occur from pressure on the nerves and spinal cord, such as arm or finger weakness, numbness or pain. Cervical radiculopathy refers to dysfunction of a nerve root caused by injury or compression of a spinal nerve root in the neck. On the other hand, cervical myelopathy refers to compression of the spinal cord within the neck.
Herniated Disc (Cervical)
Herniation of a disc is an anomalous spine condition characterized by leakage of the inner contents of the intervertebral disc, due to cracks in its outer wall. A herniated disc is commonly seen in the cervical or neck region, a condition called cervical herniated disc (CHD). CHD is followed by arm or neck pain that may arise due to compression of the spinal nerves by the protruding disc material. This condition is frequently reported in people between 30-40 years of age as well as elderly people. Treatment of CHD begins with conservative (non-surgical) methods, as reports show that around 90% of patients may return to normal activity by employing these interventions for at least 6 weeks. The patients who are not experiencing benefits from conservative interventions are recommended for surgery.
Herniated Disc (Lumbar)
Herniated disc is a condition in which the outer fibers (annulus) of the intervertebral disc are damaged causing the soft inner material of the nucleus pulposus to rupture out of its space. A herniated disc, common in the lower back (lumbar spine) occurs when there is a tear in the outer lining of the disc (annulus fibrosus). This causes the inner jelly-like material (nucleus pulposus) to leak out and place pressure on the adjacent spinal nerve root. It is the most common cause of lower back pain and pain that radiates down the leg (radiculopathy).
Adult Kyphosis-Types and Causes
Adult kyphosis, the condition of curve in the spine is categorized into the following major types:
Sciatica
Sciatica is a painful condition caused by the irritation of the sciatic nerve. Sciatica can be acute (short term), lasting for a few weeks or chronic (long term), persisting for more than 3 months. It is important to understand that in most cases, sciatica will resolve itself within a few weeks or months and rarely causes permanent nerve damage.
Spine Arthritis
Spine arthritis is a condition characterized by the inflammation, degeneration, or wearing out of cartilage in the joints of the spine. The cartilage in the spine includes the spinal discs between the vertebrae and the cartilage lining the facet joints in the back of the spine. Spinal arthritis can cause pain and stiffness in the back and neck.
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Sacroiliac joints are present in the lower back where the sacrum part of the vertebrae joins the iliac bones. The term ankylosis stands for loss of mobility of the spine, whereas spondylitis means inflammation of the spine. Therefore, ankylosing spondylitis is a condition where chronic inflammation of the spine and sacroiliac joint results in complete fusion of the vertebrae, leading to pain and stiffness in the spine.
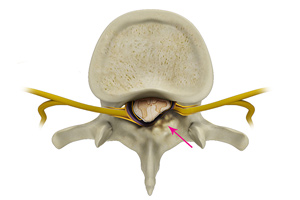
Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis is a condition caused by the vertebral column constricting and exerting pressure on the spinal cord or neural foramen (a bony tunnel through which a nerve exits the spinal cord).
Spinal Instability
Spinal instability refers to the condition of failure of the spinal column to maintain its normal structure. Normally, the spine functions to protect and provide support to the body and its internal organs. An unstable spine is incapable of holding various spinal structures such as spinal muscles, ligaments, bones, and discs in place. Mild spinal instability may resolve on its own, while a severe spinal instability may damage the spinal cord, nerve roots, and lead to spinal deformity.
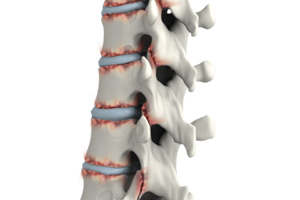
Spine Deformities
The spine or backbone provides stability to the upper part of our body. It helps to hold the body upright. It consists of a series of irregularly-shaped bones appearing in a straight line. The spine has two gentle curves, when viewed from the side and appears to be straight when viewed from the front. When these curves are exaggerated, pronounced problems can occur such as back pain, breathing difficulties and fatigue.
Spine Trauma
Spine trauma is defined as an injury or damage to any region of the spine. The spine extends from the neck to the lower back and consists of the vertebral bones which surround and protect the spinal cord. Damage to the spinal cord or spinal nerves can cause changes in sensation, strength, and other body functions.
Degenerative Spinal Conditions
A degenerative condition is a continuous deterioration of a tissue or an organ in your body over time.
Degenerative spinal conditions refer to a gradual loss of normal structure and/or function of the spine over time.
Cervical Spondylosis
Cervical spondylosis, also called arthritis of the neck, is an age-related medical condition characterized by deterioration of spinal joints, vertebrae, discs, and ligaments in your neck.
Cervical Degenerative Disorder
Cervical degenerative disc disease (DDD) is a misnomer as it is not a disease but a condition that affects the strength, resiliency and structural integrity of the intervertebral discs due to increasing age, trauma, injury, repetitive movement, improper posture, or poor body mechanics. Cervical DDD is commonly seen in adults after 50 years of age and most of them are usually not aware of their condition until they are examined for some other health condition.